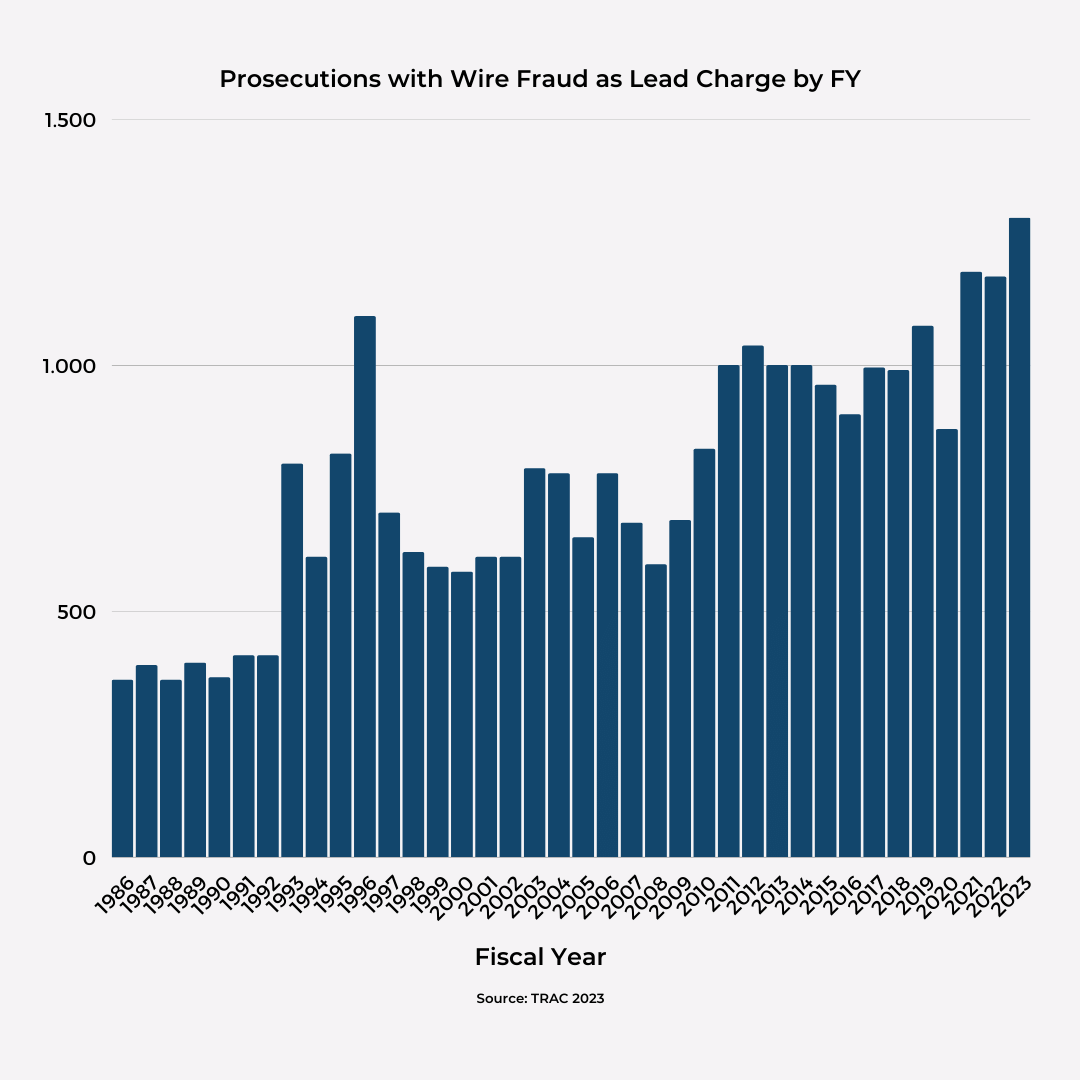
Fraud constantly takes on various deceptive forms. The most common forms are financial fraud, identity theft, online scams, and insurance fraud. Among these, wire fraud emerges as especially dangerous, characterized by illicit electronic fund transfers that can lead to significant financial losses and legal repercussions. According to the Transactional Records Access Clearinghouse (TRAC) subdivision of the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), the number of wire fraud charges is going to set a new record in 2023, highlighting the importance of understanding more about it.
What is Wire Fraud?
The meaning of wire fraud can be presented as a complex and harmful type of financial fraud that exploits electronic communication methods to orchestrate fraudulent activities. Unlike conventional fraud tactics, which often rely on physical documents or in-person interactions, wire fraud embraces modern technology. Wire fraud conspiracies are predominantly employed, such as phone calls, emails, or other digital channels to execute deceptive schemes. These schemes are carefully crafted to dupe individuals and entities into transferring money, valuable assets, or sensitive information to the perpetrators.
Examples of Wire Fraud
With boundaries constantly expanding for wire fraud definition, it started to encompass a myriad of deceptive practices that criminals employ, predominantly through wire transfer fraud. A frequently encountered scenario involves the "business email compromise" scheme, where fraudsters assume the identities of high-ranking company executives or trusted vendors. With this scheme, criminals trick employees into wiring funds to fraudulent accounts under the guise of legitimate business transactions.
Another prevalent scenario is real estate wire fraud. In this type of wire fraud, criminals get a hold of communications related to real estate transactions, manipulate transaction details, and divert substantial sums to their own accounts. Moreover, wire fraud extends its reach to scams involving lotteries and inheritances, where victims are deceived into believing they have won a prize or inheritance but are coerced into sending money.
How Does It Work?
The instigation of wire fraud typically starts with the malefactors illicitly obtaining access to sensitive information, such as email accounts or financial records. Armed with this knowledge, the perpetrators meticulously craft persuasive messages or engage in phone calls designed to psychologically manipulate the target into transferring funds or valuable assets, mostly through bank wire fraud. These deceptive communications frequently employ tactics like creating an atmosphere of urgency or making threats. With these threats, a sense of immediate crisis is instilled, which discourages victims from seeking verification of the request's authenticity.
Once the victims succumb to the pressure, the criminals furnish bank account details, often deliberately routing funds to offshore or untraceable accounts. This step of wire fraud renders it exceptionally challenging to trace or recover stolen funds, leaving victims grappling with severe financial repercussions.
Regulations Against Wire Fraud
Governments across the globe have implemented stringent regulatory frameworks and legislation to combat the widespread menace of wire fraud and safeguard the interests of consumers and businesses. These regulations are designed to dissuade potential fraudsters, simplify investigative processes, and offer legal remedies for victims.
Within the United States, wire fraud primarily falls under federal statutes, with the most prominent being the Wire Fraud Act (18 U.S.C. § 1343). This wire fraud statute renders using electronic communication, such as emails or telephone calls, for orchestrating fraudulent schemes aimed at acquiring money or assets unlawful. Convictions under this act carry severe repercussions, including substantial fines and imprisonment, with their severity changing according to the severness of wire fraud felony. Additionally, the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) administers anti-money laundering (AML) regulations and reporting mandates to oversee financial transactions. With this notion, it facilitates the identification of potential wire fraud activities.
Financial institutions, often acting as conduits for wire transfers, are subject to rigorous regulations to mitigate wire fraud risks. These institutions are required to implement robust anti-fraud mechanisms, encompassing customer identification and transaction monitoring. In the United States, the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and the USA PATRIOT Act establish criteria for financial institutions to uphold effective AML programs and report suspicious activities, in turn, contributing to the prevention and detection of wire fraud.
Given the cross-border nature of wire fraud, international cooperation plays a pivotal role in its effective containment. Numerous international accords and entities, including INTERPOL and Europol, engage in collaborative endeavors, sharing intelligence and harmonizing efforts to apprehend and prosecute wire fraud offenders worldwide. Such collaborative initiatives fortify the global response to wire fraud, enhancing the ability to enact a variety of wire fraud penalty with the help of independent justice organs.
Efforts in Wire Fraud Defense
As wire fraud continues to evolve, the defense against it has assumed greater significance. Institutions, individuals, and law enforcement agencies have taken proactive steps to formulate strategies and tactics aimed at mitigating wire fraud risks and shielding potential victims.
Advancements in Cybersecurity
Given that wire fraud frequently originates from cyberattacks or phishing attempts, fortifying cybersecurity measures is of utmost importance. Organizations make substantial investments in advanced tools such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols to protect sensitive information. Additionally, educating employees to recognize and thwart phishing attempts is instrumental in reducing vulnerability to wire fraud.
Strengthened Authentication Methods
Bolstering user authentication processes is a critical aspect of thwarting unauthorized wire transfers. Employing techniques like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and biometric verification adds layers of security, rendering it more difficult for fraudsters to gain access to accounts or impersonate legitimate individuals.
Utilization of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Harnessing the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies enables the analysis of transaction patterns and the detection of irregularities. These tools can identify suspicious behavior, such as unusual transaction amounts or sudden changes in payment destinations, alerting financial institutions and individuals to potential wire fraud attempts in real-time.
Compliance with Regulatory Frameworks
Regulatory bodies globally continue to refine regulations concerning fraud prevention and anti-money laundering. Financial institutions are obligated to adhere to these regulations, enhancing their ability to detect and report suspicious activities associated with wire fraud. Compliance mandates often encompass the implementation of comprehensive customer due diligence (CDD) procedures.
Heightened Awareness and Education
Raising awareness and providing education is vital in the fight against wire fraud. Training programs and awareness campaigns empower individuals to recognize common wire fraud tactics, encouraging them to question and verify unusual financial requests. Cybersecurity education equips individuals with the knowledge needed to identify and promptly report potential threats.
AML Transaction Monitoring Solution Against Wire Fraud
In the battle against wire fraud, Sanction Scanner emerges as a lead developer of AML compliance software. With a reputation for innovation and precision, Sanction Scanner's modern transaction monitoring tool stands as an opportunity for financial institutions seeking to safeguard their operations. This robust solution combines advanced machine learning algorithms with real-time data analysis to identify suspicious activities and potential wire fraud in real-time. To learn more about it, contact us or request a demo today.